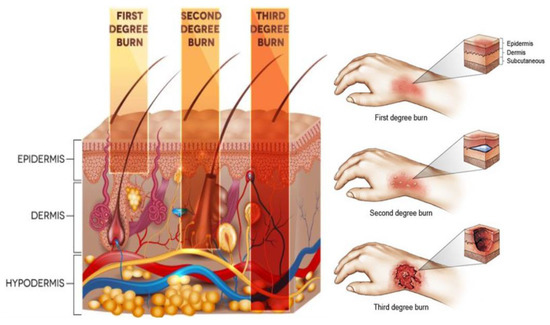
What causes a third-degree burn. Destruction of all layers of skin evident with extension into subcutaneous tissue d.
Sensors Free Full Text Assessment Of Bandaged Burn Wounds Using Porcine Skin And Millimetric Radiometry Html
What Is A 3rd Degree Burn.
. A burn that affects the entire thickness of. Third-Degree Burns Third-degree burns are the most severe type. These type of burns affect the third layer of skin and result in scarring.
Burned area covers 10 of the body D. Skin showing erythema followed by blister formation c. The outgoing nurse states that the clients pain is a 710.
Add your answer and earn points. You will easily be able to see that the burn penetrates deeply into the skin and you may even see yellowish fatty tissue in the wound bed. A third-degree burn occurs when all 3 layers of your skin are burned.
Third-degree full thickness burns Third-degree burns destroy the epidermis and dermis. They are more severe than first or second degree burns and always. Third-degree burns Third-degree burns go through both the first and second layers of skin into the third and lowest layer of the skin the hypodermis.
The nurse is receiving report on a client with chemical burns over 70 of the body. This type of burn destroys the outer layer of skin epidermis and the entire layer beneath the dermis. Your skin may be white black brown or leathery.
The dermis is rich in blood vessels and nerve fibers. Burn extends through all the skin layers and tissue. These deep burns may appear white and fleshy like burned charcoal because they affect the fatty tissue under the skin.
The left half of a persons face suffers third degree burns. The burn site appears white or charred. What is a third-degree burn.
Joes burn would best be describes as a third-degree burn. A third-degree burn is also called a full thickness burn. Burned area is on the face C.
Third-degree burns may also damage the underlying bones muscles and tendons. Areas can appear black or white and will be dry or leathery in texture. What is a third-degree burn.
Which of the following best describes a full-thickness third-degree burn. These burns usually are quite mild though they may hurt a lot. Full-thickness second-degree burns will most likely need excision and skin grafting to heal.
Third-degree burns are the most severe because they destroy the top two layers of skin affect deeper tissues and cause the most damage. This type of burn injury is often painless because the nerves have been damaged. Critical 225 3rd degree burn on face.
Why can you often not feel third-degree burns. A B C D. Third-degree burns also called full-thickness burns injure all the layers of the skin as well as the fatty tissue beneath them.
A third-degree burn will not produce blisters or look wet. Answer choices The burn might be upgraded to a third-degree burn The burn might begin to hurt less The burn might get infected The blisters will reappear almost instantly Question 5 30 seconds Q. Sunburn is a good example of a first-degree type burn.
Advertisement autsullivan3930 is waiting for your help. There is no sensation in the area since the nerve endings are destroyed. Please select the best answer from the choices provided.
Answer choices Because they damage the nerve ending in your skin Because they arent very damaging. Third-degree burns are full-thickness burns that involve the entire thickness of. But if nerve endings are damaged the burn may not hurt right away.
A third-degree burn can cause severe pain. Third degree burns or full-thickness burns are a type of burn that destroys the skin and may damage the underlying tissue. Third-degree burns result in nerve damage which reduces feeling.
This type of burn classification is reserved for the most severe burns. Max loss of skin reduced feeling almost whitish describes a third-degree burn or also called full-thickness burn. Which of the following best describes a third-degree burn.
Common causes of third-degree burns are steam hot oil grease chemicals electrical. Burned area is larger than 5 inches across B. Critical 45 3rd degree burn on face.
In most cases full thickness third-degree burns are caused by the following. It is normally a rapid process since growth hormones stimulate cell division throughout the burn area. The nurse notes that there are burns on the childs lips and singed nasal hairs.
Touching a third-degree burn usually does not cause pain. Destruction of all layers of skin evident with extension into subcutaneous tissue A child is admitted with extensive burns. Bones and muscles may also be damaged.
The rule of nines can provide a rough estimation of the percentage of body surface affected by a burn. How can the rule of nines help indicate whether a burn should be considered critical. Instead it will look dark red dry and leathery.
Blisters are a mechanism of second-degree burns to alleviate pain. Which best describes a full-thickness third-degree burn. Sweat glands continuously produce small amounts of sweat even in.
You should seek medical help right away if a second-degree partial thickness burn is larger than 3 inches in diameter or if. Which of the following statements best describes their condition. Not critical only 45 3rd degree burn.
The serum sodium is 133 K is 34 and Mag is 19. Critical with 9 3rd degree burn. The nurse should suspect that the child has An inhalation injury.
Question 9 of 10. Which of these describes a third-degree burn. Second-degree burns result in scarring.
What do burn scars look like. It is accomplished by division of cells in the dermis and begins at the center of the burn. All layers of the skin are destroyed and the damage extends into subcutaneous tissues.
Degree refers to the regions of skin affected by the burn. A third-degree burn is referred to as a full thickness burn. Doctors categorize burns by their severity or degree.
The typical causes of 3rd degree burns are radiation or corrosive chemical exposure. Blanching is sluggish or absent. The client has been averaging 80 mlhr out of urine output and receiving 125 mlhr 09 normal saline into a central venous catheter.
A burn that affects the entire thickness of the integument. Second-degree burns penetrate the epidermis and extend into the next layer of skin the dermis. The burn site appears red blistered and may be swollen and painful.
Destruction injury involving underlying structures such as muscle fascia and bone. A third-degree burn is the most serious. First-degree burns affect only the top layer of skin the epidermis.
Which best describes how resurfacing of third degree burns occurs. Erythema and pain b. These are serious burns that can affect the skins ability to grow back.

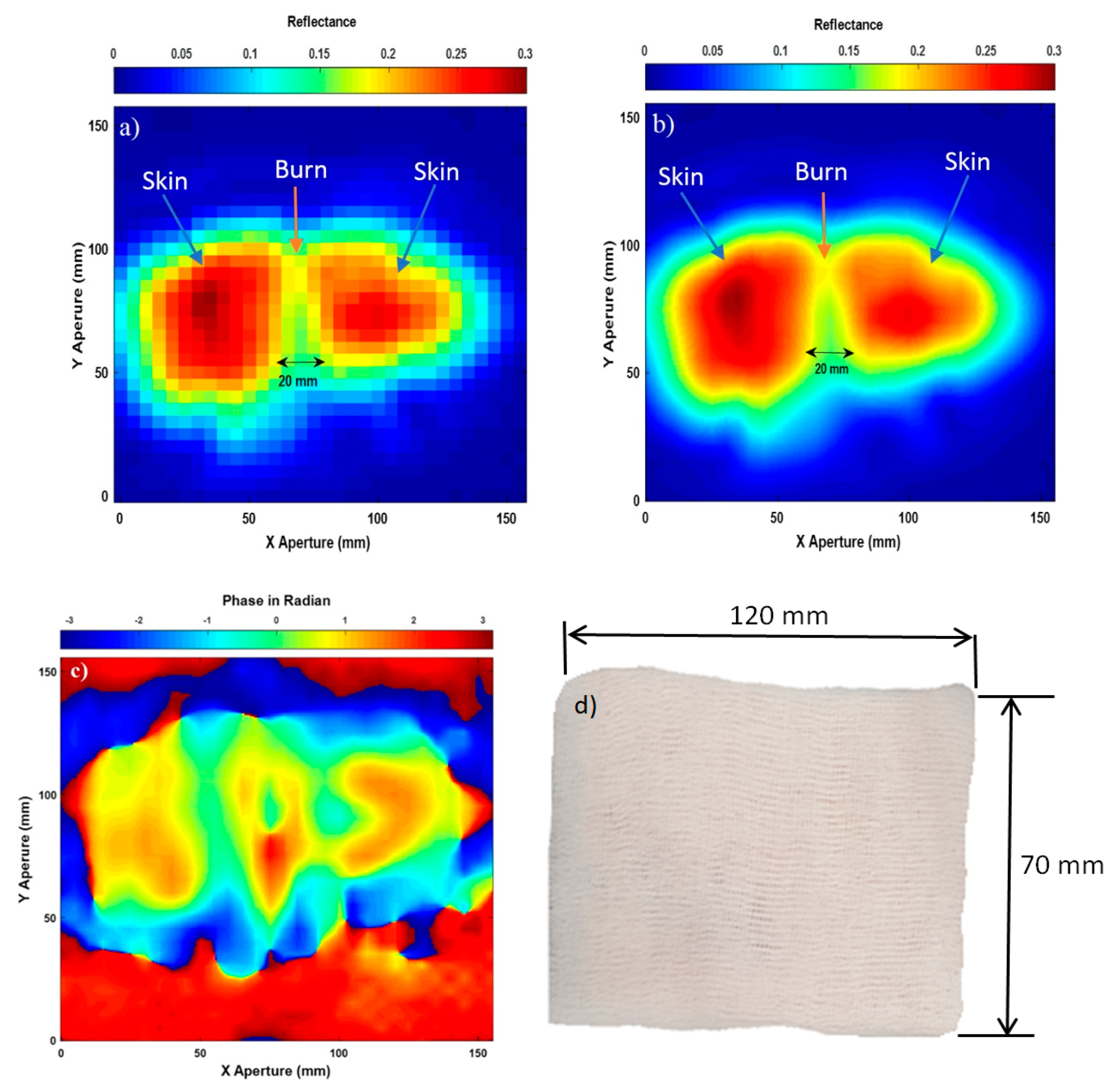
Sensors Free Full Text Synthetic Aperture Radar Imaging For Burn Wounds Diagnostics Html

0 Comments